Contents
|
|
Hyperledger vs Ethereum: Two of the hottest jobs in the blockchain market are “Ethereum developer” and “Hyperledger developer”. While there are many more platforms coming around, these two have pretty much conquered the realms of public blockchain and permissioned blockchain respectively
Reading Time: 14 mins
So, why should you learn Ethereum and Hyperledger and what are the benefits that you can gain from learning them? Well, that is the focus of today’s guide.
Contents
Hyperledger vs Ethereum
Public and Permissioned Blockchains

There are two kinds of blockchains out there:
- Public Blockchains
- Private/Permissioned Blockchains
Before we get into individual definitions and see what sets them apart, let’s get into the similarities. So, what are the similarities between public and private blockchains?
- Since they are both peer-to-peer networks, both of them offer a decentralized ecosystem.
- Every single participating node must download a copy of the blockchain.
- The blockchain is kept up-to-date through consensus protocols.
- Both the blockchains guarantee immutability.
Public Chains
All the blockchains that we are familiar with are public blockchain. Bitcoin and Ethereum have pretty much championed the cause of public blockchains. You must have pretty much guessed why they are called public blockchains. They are completely open ecosystems where anyone can take part in the ecosystem. The network also has an in-built incentive mechanism which rewards participants for taking part more thoroughly in the system.
So, what is the biggest advantage of public blockchains? Well, it is in their ability to disrupt our day-to-day activities! Think of any economic innovation that can come close to Bitcoin’s capability of disruption.
Plus think of how disruptive decentralized applications or DApps can be. In fact, this is such an important topic that we will explore more deeply in the future
However, having said that, public blockchains are extremely impractical for enterprise purposes. Let us tell you why.
- Firstly, as has been extremely well documented, the blocks in bitcoin and ethereum have a storage issue. Bitcoin has a little over 1mb of space per block which is simply not enough to run the kind of transactions and store the kind of data that enterprises require.
- Then we have the throughput problems which have been pretty well-documented. bitcoin can barely manage 7-8 transactions per second. The block confirmation time is 10 mins which just adds to the latency. Big enterprises need to deal with millions of transactions per day with near 0 latency.
- Public blockchains, especially the ones that follow the proof-of-work protocol like bitcoin require an immense amount of computational power to solve hard puzzles.
- Finally, the openness of the public chains is itself a detriment. Think about it. If you have a company which runs on a blockchain which can be accessed by malicious actors and trolls, would you really want to integrate a system like that?
Because of these reasons, public blockchains are not a practical method to go forward for enterprises.
Private/Permissioned Chains
As opposed to the public blockchains, private blockchain is not open for everyone. People who want to participate in the private chain must gain permission. This is the reason why these kinda blockchains are also referred to as “permission blockchains.”
Because of this, there are restrictions to the kind of people who can actually take part in the consensus. Access for new participants could be given by the following:
- The existing participants who are taking part in the ecosystem.
- A regulated authority.
- A consortium.
These permissioned chains have been specifically designed for enterprise needs and offer a lot of features.
Required Features of Permissioned Blockchains
#1 High Performance
Like we have already said, public chains don’t even approach 100 transactions per second. When you consider the fact that most of the enterprises like telecom and credit processors need 10,000 – 100,000 tps, that’s not really the most ideal of scenarios.
In order to reach those levels of tps, blockchains need to adopt an architectural approach which:
- Efficiently compartmentalizes different tasks.
- Uses asynchronous flows.
- Uses faster consensus protocols.
- Utilizes parallelization
- Executes itself in optimized environments.
#2 High Resilience
Enterprise blockchains must be able to come back from downtime and potential failure scenarios. To ensure high availability, they must be able to avoid issues which may lead to major outages. To have that level of resilience, the system should assume that failures are bound to happen and must be prepared to keep the system running during these situations.
Think about how traditional enterprise software survives system failure. They often utilize service replication and redundancy to make sure that they don’t go through low availability. Similarly, enterprise chains should deploy redundant peer nodes, clustered ordering services, and replicate other working blockchain network components to work seamlessly without any glitches.
#3 Privacy
Privacy and security is obviously a huge need for enterprise-level blockchains. Since these are permission blockchains, all members are known entities and carefully vetted before they enter the ecosystem.
According to this article by Coindesk:
“Digital signatures applied to all network messages enable all nodes and clients to verify the sender and validate message integrity. This is coupled with transport security to authenticate the communications endpoints and encrypt the message traffic.
Further, automatically applying encryption for the stored data completes the best practices for encrypting data in transit and at rest. When this foundation is used transparently and pervasively for all secure communications and stored ledger data, it’s a big step forward in maintaining the integrity and security of the blockchain network, preventing most hacking attacks.”
Since we are going to look into a public blockchain (Ethereum) and a permissioned blockchain (Hyperledger) we thought you should know what the difference between the two.
Ethereum: The Smart Contract Platform

While bitcoin showed the potential of the blockchain technology as a peer-to-peer decentralized payment network, many people were starting to wonder if that was the extent of the blockchain technology. One of those people happened to be Russian-Canadian programmer Vitalik Buterin. He founded Ethereum, a decentralized smart contract platform.
Developers from around the world can use Ethereum’s virtual machine to execute their smart contracts and hence run their DApps.
What are Smart Contracts?
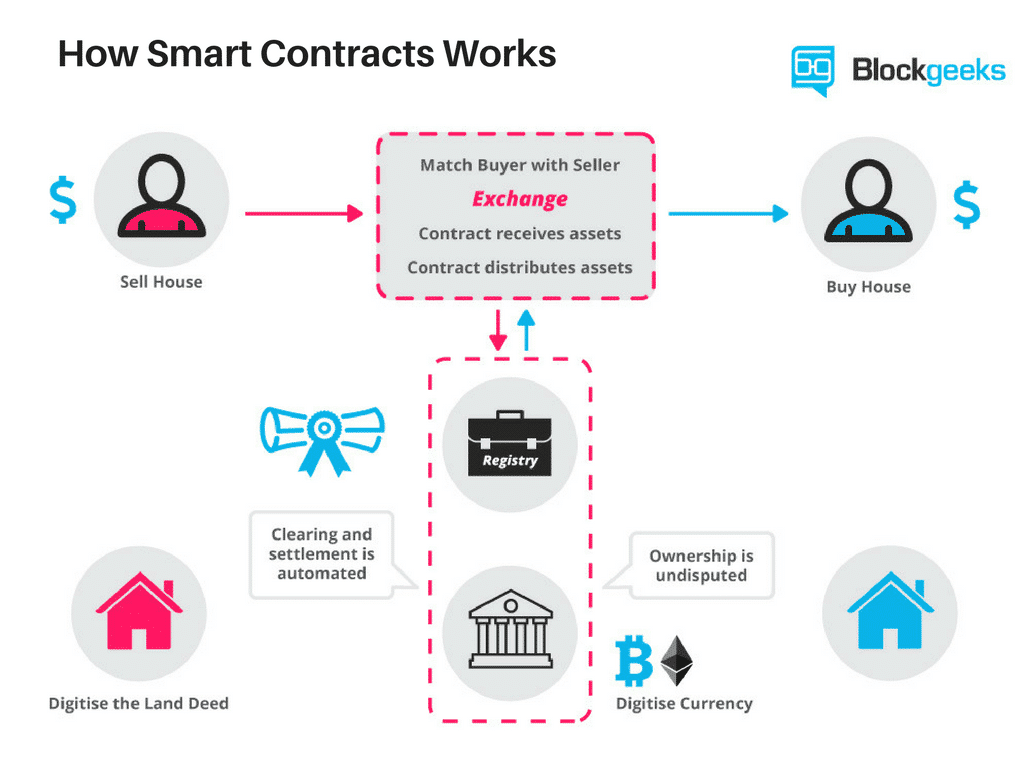
Smart contracts are automated contracts. They are self-executing with specific instructions written on its code which get executed when certain conditions are made.
You can learn more about smart contracts in our in-depth guide here.
Smart contracts are how things get done in the Ethereum ecosystem. When someone wants to get a particular task done in Ethereum they initiate a smart contract with one or more people.
Smart contracts are a series of instructions, written using the programming language “solidity”, which works on the basis of the IFTTT logic aka the IF-THIS-THEN-THAT logic. Basically, if the first set of instructions are done then execute the next function and after that the next and keep on repeating until you reach the end of the contract.
The best way to understand that is by imagining a vending machine. Each and every step that you take acts like a trigger for the next step to execute itself. It is kinda like the domino effect. So, let’s examine the steps that you will take while interacting with the vending machine:
Step 1: You give the vending machine some money.
Step 2: You punch in the button corresponding to the item that you want.
Step 3: The item comes out and you collect it.
Now look at all those steps and think about it. Will any of the steps work if the previous one wasn’t executed? Each and every one of those steps is directly related to the previous step. There is one more factor to think about, and it is an integral part of smart contracts. You see, in your entire interaction with the vending machine, you (the requestor) were solely working with the machine (the provider). There were absolutely no third parties involved.
So, Why Should You Learn Ethereum?
“Learning Ethereum” is a very vague thing to say. By learning Etheruem from a developer’s point of view, we mean learning how to create smart contracts using solidity, viper etc. The smart contract is the code behind decentralized applications or DApps.
So, when you ask why you should “learn Ethereum” you are actually asking, “why should I learn how to create DApps?”
Well, there are several reasons to do so:
#1 Decentralization is the Future
Centralization of user data is a big issue when it comes to current applications. One needs to look no further than the Facebook debacle to understand what we are talking about.

The scandal happened in early 2018 when it was discovered that Facebook sold their user data to British political consulting firm, Cambridge Analytica. Millions of users simply got their private data sold to the firm without their knowledge.
Various political organizations used information from the data breach to attempt to influence public opinion. Do you know what political decisions were made via the information gleaned from Cambridge Analytica?
- The Brexit
- Trump’s election
Literally two of the biggest political events in recent years.
It is important to understand that the sole reason why this happened was because all this data was stored inside a centralized body, in this case, Facebook.
Now the question to consider here is, what would have happened if the data was not owned by a single entity, but was instead owned by a wide area network? This would have completely taken the power away from a centralized institution like Facebook.
So, keeping this in mind, it is extremely evident that applications which have a decentralized model are the future.
#2 Built-in Payment System:
In current applications, they need to integrate their DApps with a third party payment platform like Paypal or Stripe which not only complicates their development but makes them subject to the whims of those parties as well. Eg. if Stripe goes down, then that application will not be able to accept payments for that time period.
DApps create an internal economy within their system via native tokens. Any and all transactions that happen in their ecosystem takes place via the exchange of native tokens.
#3 Transparency
Another interesting feature of the blockchain technology is transparency. Transparency basically means that whatever you store in the blockchain is going to be visible to everyone.
So, how is this useful?
Since the DApps use smart contract code as their back-end logic, blockchain’s transparency allows anyone and everyone the power to inspect and verify the code. This helps developers to find and expose vulnerabilities. This will stop hackers from stealing funds and/or data.
Ok, so now you know the benefits of learning Ethereum. But now let’s look into Hyperledger.
Hyperledger: The Enterprise Blockchains

Unlike Ethereum, “Hyperledger” doesn’t refer to a specific kind of technology. Hyperledger is the name given to a banner project by Linux Foundation for multiple blockchains and DLT technologies. The example of these hyperledger projects are:
- Hyperledger Fabric
- Hyperledger Sawtooth
- Hyperledger Iroha
- Hyperledger Indy
- Hyperledger Burrow
Hyperledger Fabric is the most popular of all these projects, so we are going to focus on that in this article. While Ethereum can be used to create projects for B2C purposes, B2b is more of a domain for Fabric. They provide a permissioned blockchain infrastructure providing a modular architecture which we will talk about a little later.
The Fabric network executes smart contracts, called chaincode, in golang, Javascript, and Java, making coding much more flexible than Ethereum. Their network consists of “Peer nodes”, and is primarily aimed at creating enterprise blockchains. Examples of industries that are using Fabric are supply chain, healthcare, banking etc. Fabric doesn’t have a native token, however, the chaincodes can build a native token of their own.
So, why should you opt to learn Hyperledger Fabric? Well, there are several reasons:
#1 What is your focus?
Firstly, you will need to ask yourself what you are focussing on. Are you looking to be employed by a well-known legacy company who wants to incorporate the blockchain technology into their operations? If yes, then you should definitely learn Hyperledger Fabric.
#2 Industry disrupting blockchains
More and more industries are understanding the power of blockchain technology. Because of its immutability and decentralization, blockchain has made information sharing between companies extremely simple and straightforward.
A perfect example of this is financial institutes. Normally, if you want to open up a new bank account, then you wll have to do your KYC from scratch. However, by incorporating a blockchain, the banks can simply share the KYC data between them.
Let’s not even get started on how blockchains can disrupt the supply chain industry and the healthcare industry. All-in-all, more and more industries are opening up to the potential of the blockchain industry.
#3 Public blockchains aren’t ideal
Like we have already mentioned before, public blockchains are not ideal for enterprise use. The two biggest problems with public blockchains are scalability and privacy. The reason is pretty simple:
- Companies deal with millions of transaction every second. That is way above what public blockchains can handle right now.
- They deal with a lot of sensitive data so they can’t just let anyone join their network.
#4 Modular architecture supporting plug-in components
Hyperledger Fabric has a modular architecture. This means that it saves the developers huge amounts of time and effort since they don’t need to build from scratch, which is a huge advantage. One of the most popular areas of modularity is “identity management.” Many companies are using an identity management module instead of building it from scratch.
Why You Should Opt For Blockchain Jobs?
Alright, so now that you know the advantages of learning Ethereum and Hyperledger, the question is, why should you spend your valuable time learning a new skill? Why should you change your career focus and enter the blockchain space? Well, let’s explore some more reasons as to why you should opt for a blockchain job. (The content idea and graphs for this section has been taken from Angel.co.)
#1 Better Pay
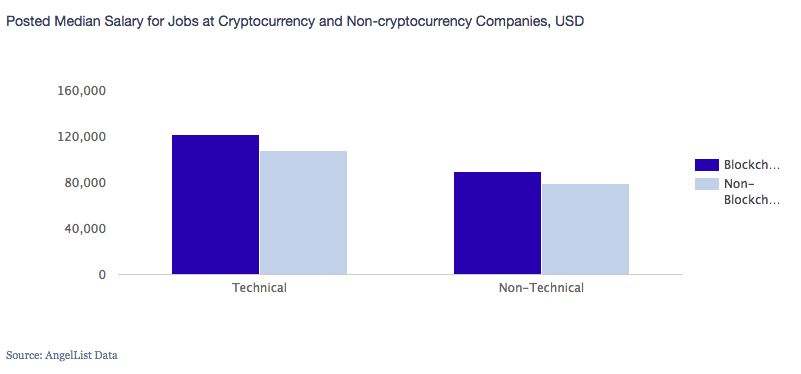
Since this is such a young field and the talent available is pretty limited, the salaries offered throughout both technical and non-technical fields are 10-20% higher than the salaries offered in a normal job.
Plus, it is also worth noting that the profit sharing models in crypto jobs are way better and the incentives a lot higher.
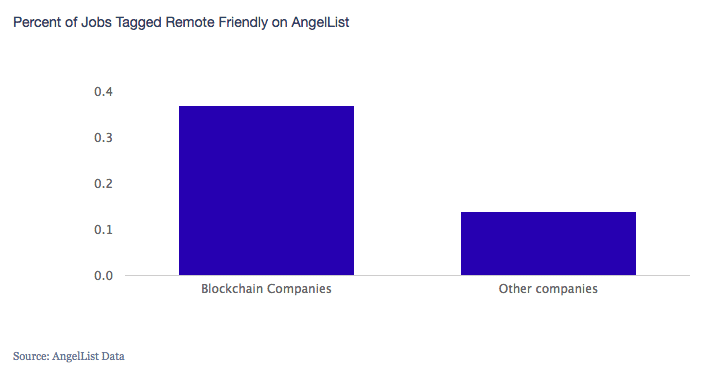
#2 Remote Flexibility
Remote jobs are on the rise and more and more people are quickly shunning the concept of an “office” and opting for location flexibility. This is another area where crypto companies outdo their legacy peers.
Plus, remember that crypto companies are far more likely to give you the “work from home” option and require you to come to work only on specific days.
#3 Employee Liquidity
This is a perk which is limited to token companies. Usually, at a startup, employees receive equity and have to wait for a liquidity event to sell shares and get Fiat currency. This may itself be a very complex process and in many scenarios, grants given by companies are very restrictive which blocks secondary transactions.
In blockchain companies, employees usually get tokens which acts as an equity-like compensation. These tokens, unlike shares, are inherently liquid, even though some of them may still have restrictions on them.
Hyperledger vs Ethereum Certification
At Blockgeeks, we are giving certifications in both Ethereum and Hyperledger.
Ethereum Certification
By taking our Ethereum accelerator program, you will:
- Be able to run your own ICO
- Have a complete understanding of Ethereum development, the blockchain, and its history
- Create and deploy smart contracts
- Be job ready and have built relationships with industry professionals
Breakdown of the Course
Let’s look into a week-by-week breakdown of the accelerator program.
Week 1: Intro to Ethereum
- Peer to Peer Network
- How bitcoin Works
- Cryptography
- Consensus and Mining
- Proof of Stake
- Linking Blocks and Merkle Proof
- History of Ethereum
Week 2: Smart Contracts
- Escrow contracts
- Auction contracts
- Election contract
- Parity Wallet Hack
- Betting contracts
- Webinar: SpankChain Hack
- Project: Write ERC20 and CrowdSale contracts
Week 3: DApp Development
- Intro to Dapps
- Truffle Migrations
- Truffle UI
- Truffle JavaScript Testing
- Truffle Solidity Testing
- Truffle Deployment
- Project: Reward point system
Week 4: Production and Security
- Buddy Works for CI
- Understanding Ethereum Gas
- Smart contract security
- Project: Crypto-kitty Clone
Bonus Materials
- A weekly live lesson with our teachers
- Direct access to teachers and dedicated support
- Weekly quizzes with feedback
- Weekly assignments and projects with feedback
- Final Blockdegree exam (Score 90% or higher and receive a personal non-fungible ERC-721 token that will identify you as a Blockgeeks Verified Blockchain Developer)
What are people saying about the Ethereum Accelerator?

By taking our Ethereum accelerator program, you will:
- Be able to build your own public blockchain project
- Create your own blockchain “identity”
- Learn the fundamentals of setting up a private blockchain network with Hyperledger Fabric
- Build a blockchain notary service API on Hyperledger Fabric that can be used to secure digital assets
Breakdown of the Course
Let’s look into a week-by-week breakdown of the accelerator program.
Week 1: Managing your Blockchain Identity
- Peer to Peer Network
- Cryptography
- Cryptoeconomics of Bitcoin
- Incentives on the Blockchain
- Consensus and Mining
- Project: Create your own blockchain “identity”
Week 2: Creating Your Own Private Blockchain & Notary Service
- History of Ethereum
- History of bitcoin
- Public and Private Chains
- Intro to Hyperledger Fabric
- Environment Setup
- Hyperledger Fabric Network
- Deploying Your First Network
- Project: Build a blockchain notary service API on Hyperledger Fabric
Week 3: Architecture, Supply Chain & Data Auditing
- Chaincode for Developers
- Chaincode for Operators
- Project: Create your own full node and interface back-end services
- Project: Modify your chaincode to support change of ownership
Week 4: Capstone Project
- Project: Build your own public blockchain project
Bonus Materials
- A weekly live lesson with our teachers
- Direct access to teachers and dedicated support
- Weekly quizzes with feedback
- Weekly assignments and projects with feedback
- Final Blockdegree exam (Score 90% or higher and receive a personal non-fungible ERC-721 token that will identify you as a Blockgeeks Verified Blockchain Developer)
What are people saying about the Hyperledger Accelerator?
Having read everything, if you think this program will be valuable for you, then click here and register.
Should You Choose These Programs?
- Due to the nature of our program, it will not be suitable for every applicant. Therefore not every applicant will be accepted into the program. We are not doing this to be mean, but we only want to save you time, money and frustrations. Therefore it is strongly recommended that you have some kind of prior programming basics, whether that’s javascript, python, or something else.
- We are also limiting the spots in the program to 25 qualified people this semester. We do this in order to make sure every student succeeds in the program
Hyperledger vs Ethereum: Conclusion
So there you have it. Have we convinced you to move into the blockchain space if you weren’t going to do that already? Do you think that this will be an interesting skill to add to your arsenal?
If yes, then come on over and join our courses. Whether it be Ethereum or Hyperledger, we’ve got you covered!





If, as I understand it, Hyperledger is used to build a Permissioned (private) projects, why would the capstone for the Hyperledger course be building a Public Blockchain?
How do the accelerator programs compare to the courses I can do as a owner of the blockgeeks membership?