Contents
|
|
Cardano is a rapidly growing blockchain platform that aims to provide a secure and scalable infrastructure for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. With the introduction of new crypto tokens, such as Ethereum, and the support of stake pools by Coinbase, Cardano is poised to revolutionize the blockchain industry. With its innovative approach, Cardano offers a unique combination of research-driven design principles, advanced technology, and strong community involvement in the development of new crypto tokens and decentralized finance apps on the ethereum platform. The idea behind Cardano is to create a more secure and scalable blockchain ecosystem.
Built on scientific philosophy and peer-reviewed academic research, Cardano sets itself apart by focusing on scalability, sustainability, and security in the crypto industry. With its innovative approach, Cardano aims to provide a decentralized finance app platform that rivals Ethereum. By implementing a stake pool system, Cardano ensures the security and integrity of its network. The platform utilizes a layered architecture that separates the settlement layer from the computation layer, allowing for flexibility and adaptability in meeting the needs of various industries. This architecture is especially beneficial for apps and stakeholders who work with Ethereum, as it enables them to easily integrate and interact with the Ethereum network. Additionally, the platform supports the creation and management of stake pools, providing a secure and efficient way for users to participate in staking activities.
We will also discuss the advantages that Cardano brings to developers and users alike, including its robust consensus mechanism, low transaction fees, commitment to transparency, and its compatibility with ethereum. Additionally, Cardano provides a stake pool system that allows users to actively participate in the network’s work.
Join us as we dive into the world of Cardano, ethereum, and stake pools, and discover why Cardano has garnered significant attention within the blockchain community. Let’s explore how Ethereum, a groundbreaking stake pool platform, is poised to revolutionize industries while maintaining a strong focus on security and sustainability.
Contents
The Origins of Cardano
Cardano was conceptualized by Charles Hoskinson who happens to be one of the co-founders of Ethereum.
Pictured above: Charles Hoskinson. Image Credit: IOHK.
While Ethereum does an admirable job as a smart contract platform, according to Hoskinson it is a second generation blockchain (more on this later) and needed evolution. What makes Cardano extremely remarkable is the sheer amount of care that goes into its upkeep. There are three organizations which work full time to develop and take care of Cardano.
They are:
- The Cardano Foundation.
- IOHK.
- Emurgo.
The Cardano Foundation is a not-for-profit regulated entity that is the custodial organization of Cardano. Their main function is to “standardize, protect, and promote the Cardano Protocol technology”.
In 2015, along with Jeremy Wood, Hoskinson found IOHK (Input Output Hong Kong). IOHK is a “research and development company committed to using the peer-to-peer innovations of blockchain to build accessible financial services for all.” They have been contracted to build, design, and maintain Cardano until 2020.
Finally, we have Emurgo. Emurgo is a Japanese company that “develops, supports, and incubates commercial ventures who want to revolutionize their industries using blockchain technology.” Much of IOHK’s funding comes from a 5-year contract with Emurgo.
These three organizations work in synergy to make sure that Cardano development is going on at a good pace. So, now you are probably thinking as to why Cardano was required in the first place. Cardano describes itself as a 3rd generation blockchain. Let’s see what does that mean?
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Cardano is a blockchain platform that was founded in 2015 by Charles Hoskinson. It was launched in 2017.
- Cardano aims to be a decentralized application (DApp) development platform with a multi-asset ledger and verifiable smart contracts.
- Cardano runs on the proof-of-stake Ouroboros consensus protocol.
- The primary cryptocurrency of Cardano is called “Ada.”
- Cardano oversight is decentralized and shared by the Cardano Foundation, IOHK, and EMURGO.
The Three Generations of Blockchain
According to Charles Hoskinson, we have gone through three generations of blockchains.
Generation 1: Bitcoin and Money Transfer
Bitcoin was created because everyone was asking the same questions.
Will it be possible to create a form of money which can be transferred between two people without any middleman?
Will it be possible to create a decentralized money which can function on something like the blockchain?
Satoshi Nakamoto answered these questions when he created bitcoin. We finally had a decentralized monetary system which can transfer money from one person to another.
However, there was a problem with bitcoin which is a problem with all first generation blockchains.They only allowed for monetary transactions, there was no way to add conditions to those transactions.
Alice can send Bob 5 BTC, but she couldn’t impose conditions to those transactions. Eg. She couldn’t tell Bob that he will get the money only if he performed certain tasks.
These conditions would need extremely complicated scripting. Something was required to make the process more seamless.
Generation 2: Ethereum and Smart Contracts
And that “something” was a smart contract.
What is a smart contract?
Smart contracts help you exchange money, property, shares, or anything of value in a transparent, conflict-free way while avoiding the services of a middleman.
Vitalik Buterin’s Ethereum is easily the stalwart of this generation. They showed the world how the blockchain can evolve from a simple payment mechanism to something far more meaningful and powerful.
However, this generation had some problems too.
As more and more interesting use cases of the blockchain were coming out, they were getting more and more acceptance.
The problem was though, these generations of blockchain didn’t really have good provisions for scalability. Along with that, the governance system of these blockchains were not really that well thought out. Case in point, the Ethereum and Ethereum Classic split, according to Hoskinson, is a classic example (no pun intended) of bad governance.
This is where the third generation comes in.
Generation 3: Cardano
Hoskinson knew that the blockchain needed to evolve even more. He took the positive elements from the first two generations of blockchain and added some elements of his own. What came about from that was Cardano.
The three elements that Cardano wanted to solve were:
- Scalability.
- Interoperability.
- Sustainability.
As mentioned before, Cardano is unique in the sense that it is built on scientific philosophy and peer-reviewed academic research. All the engineering that goes into it has the ultimate goal of being “High Assurance Code”. This is done to make sure that there is much higher belief in the quality of the code used (more on this later when in the “Haskell and Plutus” section). This, according to Hoskinson, will prevent future cases like the ETH-ETC split from happening.
So, before we go any further, let’s explore the philosophy of Cardano.
The Philosophy of Cardano
The Cardano team wants to adhere to a set of principles and philosophies. They did not set out with a proper roadmap or a white paper. Instead, they focused on embracing a “collection of design principles, engineering best practices, and avenues for exploration.”
The following are these principles and they are taken directly from the Cardano website.
- Separation of accounting and computation into different layers.
- Implementation of core components in highly modular functional code
- Small groups of academics and developers competing with peer-reviewed research
- Heavy use of interdisciplinary teams including early use of InfoSec experts
- Fast iteration between white papers, implementation and new research required to correct issues discovered during review
- Building in the ability to upgrade post-deployed systems without destroying the network
- Development of a decentralized funding mechanism for future work
- A long-term view on improving the design of cryptocurrencies so they can work on mobile devices with a reasonable and secure user experience
- Bringing stakeholders closer to the operations and maintenance of their cryptocurrency
- Acknowledging the need to account for multiple assets in the same ledger
- Abstracting transactions to include optional metadata in order to better conform to the needs of legacy systems
- Learning from the nearly 1,000 altcoins by embracing features that make sense
- Adopt a standards-driven process inspired by the Internet Engineering Task Force using a dedicated foundation to lock down the final protocol design
- Explore the social elements of commerce
- Find a healthy middle ground for regulators to interact with commerce without compromising some core principles inherited from Bitcoin.
Now that we have seen the philosophy, let’s look at the three elements in detail that Cardano aims to solve.
Element #1: Scalability
When people say “scalability” they invariably think of transactions processed per second or throughput. However, according to Hoskinson, that’s just one part of the problem. Total scalability is a three-headed hydra so to speak. One needs to take care of three separate elements:
- Transactions per second/ Throughput
- Network.
- Data Scaling.
#1 Throughput
Many articles have been written on the lack of throughput in Bitcoin and Ethereum. Bitcoin manages 7 transactions per second and Ethereum manages 15-20. This is absolutely not acceptable for a financial system.
Cardano hopes to solve this problem with their consensus mechanism, Ouroboros. It is a provably secure proof-of-stake algorithm. Ouroboros was actually peer-reviewed and approved during Crypto 2017.
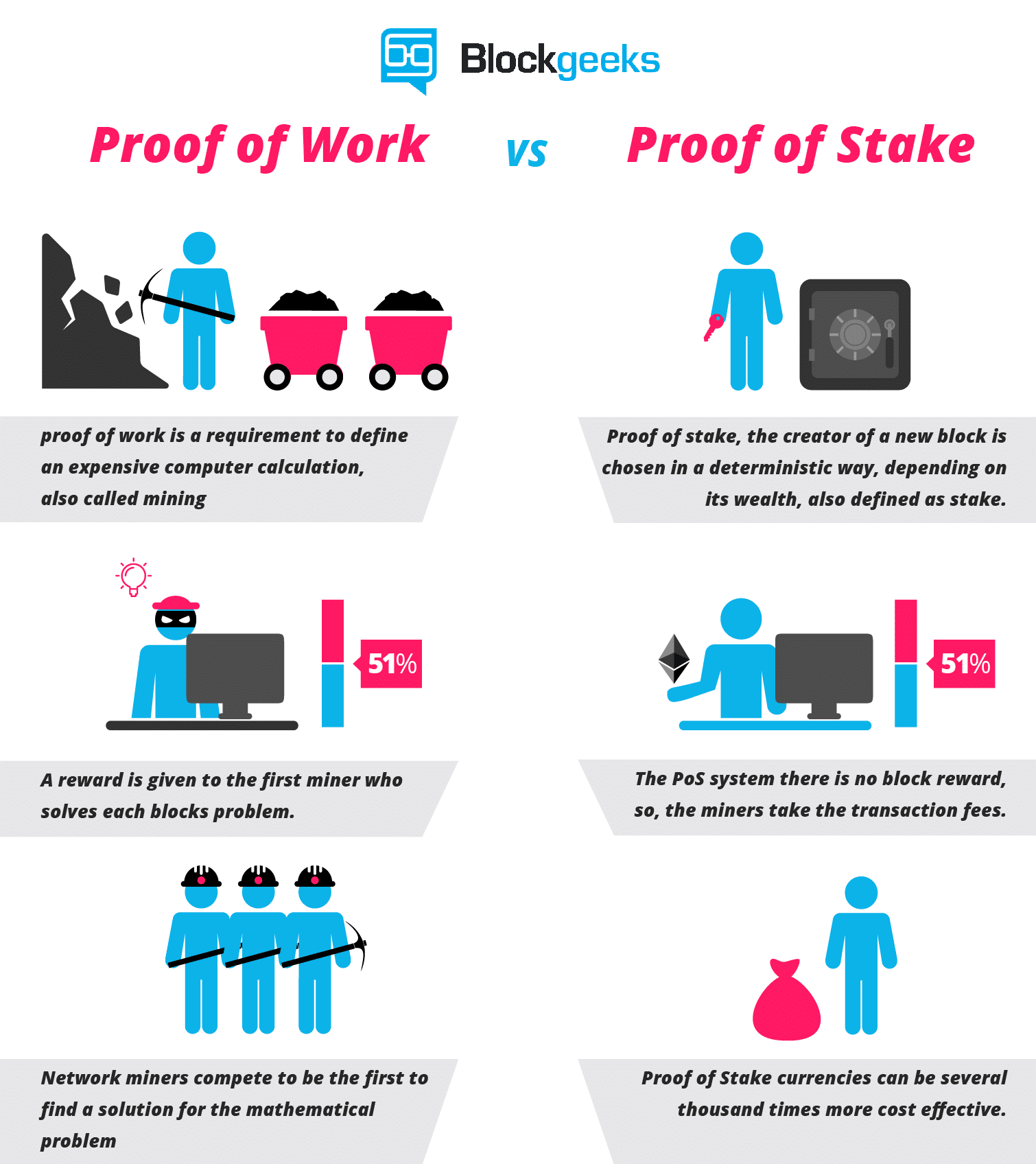
Ouroboros, as stated earlier is a proof-of-stake algorithm. Before we get deeper into the mechanism, we must know what proof of stake is.
Bitcoin and Ethereum (for now at least) follows the proof-of-work protocol.
Proof-of-work as a process has the following steps to it:
- The miners solve cryptographic puzzles to “mine” a block in order to add to the blockchain.
- This process requires an immense amount of energy and computational usage. The puzzles have been designed in a way which makes it hard and taxing on the system.
- When a miner solves the puzzle, they present their block to the network for verification.
- Verifying whether the block belongs to the chain or not is an extremely simple process.
That, in essence, is what the proof-of-work system is. Solving the puzzle is difficult but checking whether the solution is actually correct or not is easy. This is the system that Bitcoin and Ethereum (till now) have been using. However, there are some fundamental flaws in the system.
The problem with proof of work.
As it turns out, there are quite a few problems with proof-of-work.
- First and foremost, proof of work is an extremely inefficient process because of the sheer amount of power and energy that it eats up.
- People and organizations that can afford faster and more powerful ASICs usually have a better chance of mining than the others.
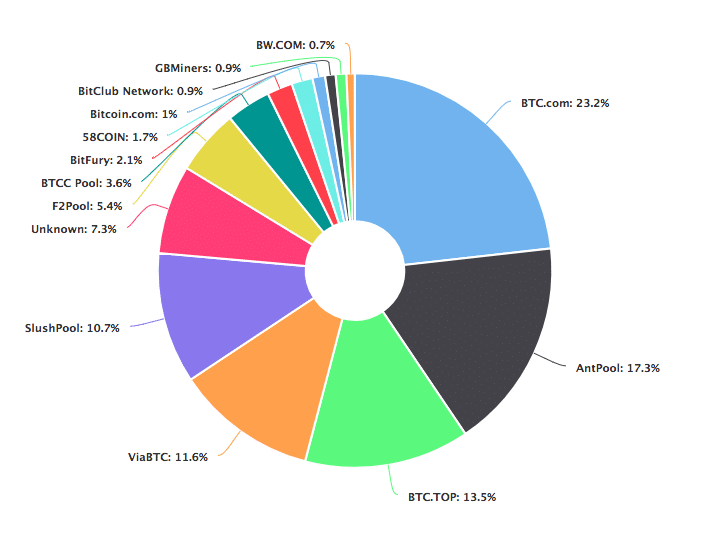
- As a result of this, bitcoin isn’t as decentralized as it wants to be. Let’s check the hashrate distribution graph:
- Image Credit: Blockchain.info
As you can see, ~75% of the hashrate is divided among 5 mining pools alone!
- Theoretically speaking, these big mining pools can simply team up with each other and launch a 51% on the bitcoin network.
So, to solve these problems, Ethereum looked to Proof of Stake as a solution.
What is proof of stake?
Proof of stake will make the entire mining process virtual and replace miners with validators.
This is how the process will work:
- The validators will have to lock up some of their coins as stake.
- After that, they will start validating the blocks. Meaning, when they discover a block which they think can be added to the chain, they will validate it by placing a bet on it.
- If the block gets appended, then the validators will get a reward proportionate to their bets.
Now that we know what POS looks like, let’s look at the mechanism behind Ouroboros.
Cardano: Ouroboros Underneath the Hood
Ouroboros looks at the distribution of the tokens in the ecosystem and from a source of random numbers, it divides the world into epochs. Each epoch is then divided into slots. Each epoch lasts for a very short of time ~20 seconds.
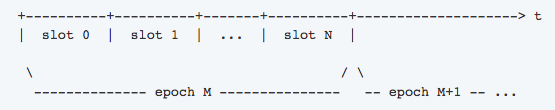
Image credit: Cardano Docs
Each slot then gets its own slot leader, who is randomly chosen.
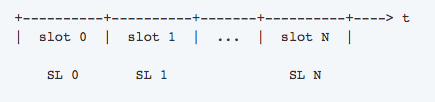
The Slot leader act like miners does in a POW protocol in the sense that they are the ones who choose the blocks that get added to the blockchain. They can, however, add only one block.

If a slot leader somehow misses their chance and doesn’t choose the block, they miss their opportunity and will have to wait till they become slot leaders again. It is ok for one or more slots to remain empty (without generated blocks), but the majority of the blocks (at least 50% + 1) must be generated during an epoch.
As you can see, the slot leaders have a very important role to play in the ecosystem. To be considered for qualification, one must own 2% stake in Cardano. These stakeholders are called electors and they are the ones who elect the slot leaders for the next epoch during the current epoch. The more stake the stakeholder has in the system, the more chance they get to be elected as slot leaders.
Now, since the slot leaders have a lot of power, special care must be taken to make the election as unbiased as possible. There must be some amount of randomness involved. This is why a multiparty computation (MPC) is done to achieve some form of randomness.
In this MPC approach, each elector performs a random action called “coin tossing” and after that shares their results with other electors. Though the results are randomly generated by each elector, they eventually agree on the same final value.
The election is divided into three phases:
- Commitment Phase.
- Reveal Phase
- Recovery Phase.
Let’s explore what happens within each phase.
Commitment Phase
Firstly, an elector generates a secret random value and then forms a “commitment”. The commitment is a message that contains encrypted shares (keep this in mind for the recovery phase) and a proof of secret.
After that, an elector signs the commitment with their private key and specifies the epoch number and attaches their public key. Doing this solves two purposes:
- Everybody can check who created this commitment (since it has the public key attached to it).
- They can check which epoch it belongs to.
After this is done, the elector sends their commitments to other electors. Eventually, each elector collects the other elector’s commitments (The commitments get put into the block and become part of the blockchain).
Reveal Phase
The second phase is the reveal phase.
Think of commitments like a locked box that has a secret in it and there is a special value that unlocks the box. This special value is called an “opening”. This is what this phase is all about, the electors send their “opening”. These openings are also put into the block and then becomes part of the blockchain.
Recovery Phase
Finally, we have the recovery phase.
By this time, an elector has both commitments and openings. However, some electors may act maliciously and publish their commitment without the opening. Basically, give the locked box without the passphrase.
In order to circumnavigate this, the honest electors can post all the encrypted shares (as mentioned in commitment phase) and simply reconstruct the secrets. This way, even if certain electors act in a malicious manner, the system will still work. This is how Ouroboros gets its Byzantine Fault Tolerance.
Eventually, an elector verifies that the commitments and openings match and when that happens, the secrets from the commitments are extracted which forms a seed. The seed is a randomly generated byte string.
All the electors now possess this seed.
So, let’s pause for a second and check where we are right now.
We are electing slot leaders for the next epoch. In order to make sure that the election is as unbiased as possible we needed some sort of randomness. The “seed” provides us with this randomness. Now it is time to select the Slot Leaders.
To do that we will use the Follow the Satoshi (FTS) algorithm.
Cardano: The FTS Algorithm
The name of the algorithm comes from Satoshi Nakamoto, the unknown creator of Bitcoin.

Image credit: Cardano Docs
The FTS basically selects a random coin from the stake. Whoever owns that coin becomes the slot leader. It is that straightforward!
This is why, the more stake one has in the system, the more chances they have of winning this lottery.
The slot leaders will also have the power to not only choose the blocks in the main blockchain but to choose blocks in other blockchains inside the Cardano ecosystem as well.
#2 Network
So how does Network factor into scalability?
Simple… bandwidth.
The transactions carry data. So as the number of transactions increases so does the requirement for network resources.
The notion is pretty straightforward: If a system is to scale up to millions of users, the network will need 100s of terabytes or exabytes of resources to sustain itself.
As such, it is impossible to maintain a homogenous network topology. What does that mean?
In homogenous network topology, every node in the network relays every message. Skype is an example of such a network where most of the value is taken from a single class of users who are all interested in placing a phone call.
However, in a decentralized network, that can become impractical for scaling up. All the nodes may not have the resources required to relay the information in an effective manner.
To solve this issue, Cardano is looking at a new type of technology called RINA, Recursive Inter-Network Architecture created by John Day. It is a new type of structuring networks using policies and ingenious engineering principles.
RINA’s goal is to create a heterogeneous network which promises to give:
- Privacy.
- Transparency.
- Scalability.
It does so in a way where you can guess how the network is going to organize in a formal capacity. It is hoped that it will seamlessly interoperate with TCP/IP protocols. Cardano hopes to implement this in part by 2018 and completely by 2019.
According to Wikipedia, “RINA inherently supports mobility, multi-homing and Quality of Service without the need for extra mechanisms, provides a secure and programmable environment, motivates for a more competitive marketplace, and allows for a seamless adoption.”
#3 Data Scaling
Finally, we have data scaling.
Think about this.
Blockchains store things for eternity. Every little piece of data, relevant or not gets stored in the blockchain for eternity. As, the system scales up and more and more people come in, with the sheer influx of data the blockchain gets more and bulkier.
Now, remember that a blockchain runs because it comprises of Nodes. Each node is a user who stores a copy of the blockchain in their system.
You see where the problem is right?
As the blockchain gets bulkier, it will demand more space, and that is unreasonable for a normal user with a normal computer.
The way Cardano wants to solve this problem is by implementing a simple philosophy, “Not everyone needs all the data.”
E.g. if Alice and Bob engage in a transaction, it may not be relevant to anyone else in the network. The only thing they need to know is that the transaction happened and that it was legitimate.
The techniques that Cardano is looking into are:
- Pruning.
- Subscriptions
- Compression.
If they are applied synergistically, then it may actually substantially reduce the amount of data that a user needs to have.
Along with this, there is also the concept of Partitioning. What that actually means is that instead of having a whole blockchain, a user can simply have a chunk of the blockchain and greatly reduce the amount of data they need to store. Which they are hoping to do via sidechains (more on this later).
Cardano’s aim here is to use all this information to compress the data that the users need to consume without compromising on security or the assurances that their transactions have gone through properly. Research on this has started in the University of Edinburgh.
Element #2: Interoperability
Now we have seen how the Scalability side of Cardano works, we now come to the second pillar: Interoperability. The long and short of interoperability is, as Charles Hoskinson puts it, there won’t be one token to rule them all.
Let’s look at the current ecosystem. In the cryptosphere, we have different crypto coins such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, Litecoin etc. Similarly, in the legacy financial world, we have systems like the traditional Banks which use SWIFT, ACH etc.
The problem lies in the fact that it is extremely difficult for these individual entities to communicate with one another. It is tough for bitcoin to know what is going on in Ethereum and vice-versa. This becomes doubly difficult when banks try to communicate with the cryptos.
This is why, the crypto exchanges, which provide a portal between cryptos and banks become so powerful and important. However, there in itself lies a problem. Exchanges are not a decentralized entity and are extremely vulnerable.
- They can get hacked.
- They can blackout for long periods for system upgradation. This is basically what happened to Binance recently.
Plus, there is another area where this miscommunication between the legacy world and the crypto world can lead to a disastrous result: ICOs.
In ICOs, an entity gets millions of dollars in exchange for their tokens, however, saving that money in their bank accounts can become difficult. The banks would obviously want to know where all that money came from and who were the ones who provided that money which is something that is near impossible to provide.
A more elegant and risk-free solution to interoperability was needed.
A third-generation cryptocurrency coin must provide an ecosystem where each individual blockchain can communicate with another blockchain and with external legacy financial systems.
So, let’s looks at how Cardano plans to do increase interoperability in both the crypto world and the legacy world.
The Crypto World: Inter-Chain Communication and SideChains
Cardano’s vision is to create an “internet of blockchains”. Imagine an ecosystem where Bitcoin can flow into Ethereum and Ripple can seamlessly flow into Litecoin without the need to go through centralized exchanges. This is why cross-chain transfers are something that Cardano wants to implement without any middlemen
One way that Cardano wants to do this is by implementing sidechains.
Sidechain as a concept has been in the crypto circles for quite some time now. The idea is very straightforward; you have a parallel chain which runs along with the main chain. The side chain will be attached to the main chain via a two-way peg.
Cardano will support sidechains based on the research by Kiayias, Miller, and Zindros (KMZ) involving “non-interactive proofs of proofs of work”.
According to Hoskinson, the idea of sidechains comes from two things:
- Getting a compressed version of a blockchain.
- Creating interoperability between chains.
What will Cardano be used for?
When it comes to increasing the interoperability with the legacy world, Cardano wants to focus on the three obstacles that make the crypto world incompatible with the legacy world:
- Metadata.
- Attribution.
- Compliance.
Obstacle #1: Metadata
Metadata means the story behind the transaction.
If Alice were to spend 50 USD, the metadata of that could be as follows:
- What did Alice spend the money on?
- Who did Alice give that money to?
- Where did she spend the money?
While that is not that well planned out in the cryptocurrency space, it is extremely essential in the legacy banking world. In fact, this is one of the main reasons why most entities struggle post ICOs. They simply don’t have the metadata required to provide the banks.
In the legacy world, the metadata is extremely important. Here are the purposes that it serves:
- Resource discovery and identification.
- Effective electronic data organization.
- Tells us how data is exchanged among various systems and hence improves interoperability.
- Very useful in resource protection. Helps identify the data’s characteristics and behavior for it to be replicated if needed.
However, the problem with metadata is that it is extremely personal and since the data is stored in the blockchain on a permanent and transparent basis, we have a situation where extremely private information can be permanently affixed to the blockchain.
One of the main things that Cardano is researching on is how to selectively attach metadata to the chain.
Obstacle #2: Attribution
Similar to metadata, via attribution the names of the people involved in the transactions gets known. Basically, who all are a particular transaction attributed to?
If the blockchain permanently fixes attribution to itself, it will greatly compromise on the privacy of the individuals involved.
Hence, Cardano plans to empower their users to hand out attribution as and when it is required.
Obstacle #3: Compliance
The third obstacle is “Compliance”.
Compliance includes factors like: KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti Money Laundering), ATF (Anti Terrorist Financing) etc.
Compliance is used to check the legitimacy of a transaction. Basically, if Alice pays Bob $50, compliance is used to make sure that the transaction is not done for any nefarious purposes.
While the crypto world hasn’t really done much on this front, it is extremely critical in the banking world where the history and legitimacy of each transaction must be known.
What Cardano is researching on is how to use Metadata and Attribution in conjunction with Compliance to help their users whenever they need to interact with the banks.
Element #3: Sustainability
Finally, we come to the third pillar, sustainability.
According to Hoskinson, this is hands down the toughest one to solve. It basically means, how is Cardano planning to pay for its future development and growth?
Usually, when some development needs to be done in the system and grants are required, there are a couple of things that can happen:
- Patronage.
- ICOs
However, both of them have an issue.
With patronage, you have the problem of a possible centralization. If a big company gives a huge amount of grant to a blockchain company, they may direct the way the developments turn out in the system.
With ICOs, it’s like a sudden jolt of money without any sustainable model and it adds a complete unnecessary token to the ecosystem.
Something different and more sustainable needs to be done.
In this sense, Cardano is planning to take inspiration from Dash and create a treasury.
How will the treasury work?
Every time a block is added to the chain, a part of that block reward will be added to the treasury.
So, if someone wants to develop and bring some changes to the ecosystem, they submit a ballot to the Treasury to ask for grants.
The stakeholders of the Cardano ecosystem then vote and decide if the ballot should be granted or not.
If they do, the ballot submitter gets the grant for development.
This system has a couple of major advantages:
- The treasury keeps on filling up as more and more blocks are discovered.
- It is directly proportional to the size of the network. Bigger the network, more the resources available and the voting system also becomes more decentralized.
However, there are some major obstacles in the way before this gets utilized.
- A fair voting system needs to be established.
- Voters should have an incentive to vote and participate in the system.
- Everyone’s vote should have some value so that a “Tragedy of Commons” type situation doesn’t happen.
- The process of submitting ballots should be easy and straightforward.
- The entire process should be as decentralized as possible.
As of right now, Cardano has identified a system that they can possibly use, which combines liquid democracy with an incentivized treasury model.
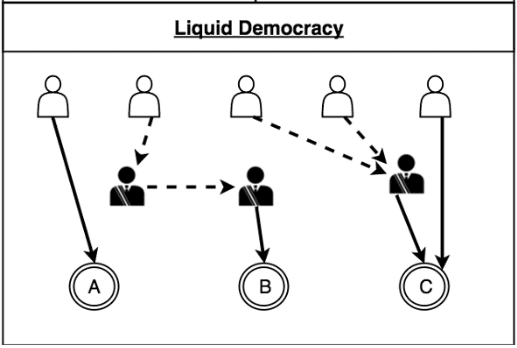
Cardano: how does liquid democracy work?
It is a system that fluidly transitions between direct democracy and representative democracy.
The process has the following features:
- People can vote on their policies directly.
- People can delegate their voting responsibilities to a delegate who can vote on their policies for them.
- The delegates themselves can delegate their voting responsibilities to another delegate who can vote on their behalf. This property wherein a delegate can appoint their own delegate is called transitivity.
- If a person, who has delegated their voting doesn’t like the vote that their delegates have chosen, then they can simply take back their vote and vote on the policy themselves.
So, what are the advantages of liquid democracy?
- The opinion of each individual person counts and plays a part in the final policy creation.
- In order to become a delegate, all that one needs to do is to win a person’s trust. They don’t need to spend millions of dollars on expensive election campaigns. Because of this, the barrier to entry is relatively low.
- Because of the option to oscillate between direct and delegated democracy, minority groups can be more fairly represented.
- Finally, it has a scalable model. Anyone who doesn’t have the time to vote on their policies can simply delegate their voting responsibilities.
Haskell and Plutus
Cardano’s coding is done in Haskell while their smart contracts will be coded in Plutus. To understand why that is such a unique approach, we need to understand some basics about programming languages.
When it comes to languages, they belong to two families:
- Imperative
- Functional.
Imperative Programming Languages
In an imperative approach, the coder needs to put down all the steps that the computer needs to take in order to reach a goal. All of our traditional programming languages like C++, Java and even Solidity are imperative programming languages. This kind of programming approach is also called algorithmic programming.
Let’s take an example of what we mean by that. Let’s look at C++. Suppose we want to add 5 and 3.
- int a = 5;
- int b = 3;
- int c;
- c= a + b;
So, as you can see, the addition process takes over multiple steps and each step is constantly changing the state of the program as they are all being executed in turn individually.
An addition process took four steps and the steps are:
- Declaring an integer a and assigning the value 5 to it.
- Declaring an integer b and assigning the value 3 to it.
- Declaring an integer c.
- Adding the values of and b and storing them in c.
Cardano Functional Programming Languages
The second family of programming languages is Functional languages. This style of programming was created to build a functional approach to problem-solving. This kind of approach is called declarative programming.
So, how does functional programming work?
Suppose there is a function f(x) that we want to use to calculate a function g(x) and then we want to use that to work with a function h(x). Instead of solving all of those in a sequence, we can simply club all of them together in a single function like this:
h(g(f(x)))
This makes the functional approach easier to reason mathematically. This is why functional programs are supposed to be a more secure approach to smart contract creation. This also aids in simpler Formal Verification which pretty much means that it is easier to mathematically prove what a program does and how it acts out. This gives Cardano its “High Assurance Code” property.
Let’s take a real-life example of this and see why it can become extremely critical and even life-saving in certain conditions.
Suppose, we are coding a program that controls air-traffic.
As you can imagine, coding such a system requires high degree of precision and accuracy. We can’t just blindly code something and hope for the best when people’s lives are at risk. In situations like these, we need a code that can be proven to work to a high degree of mathematical certainty.
This is precisely why the functional approach is so desirable.
And that is exactly what Cardano is using Haskell to code their ecosystem and Plutus for their smart contracts. Both Haskell and Plutus are functional languages.
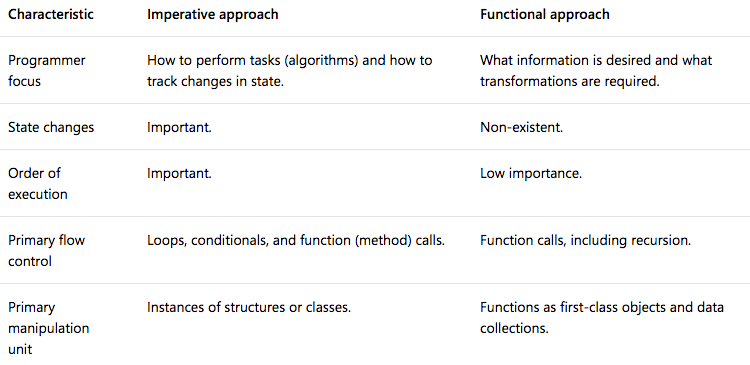
The following table compares the Imperative approach with the Functional approach.
Image Credit: Docs.Microsoft.com
So, let’s let’s look at the advantages of the functional approach:
- Helps with creating high assurance code because it is easier to mathematically prove how the code is going to behave.
- Increases the readability and maintainability because each function is designed to accomplish a specific task. The functions are also state-independent.
- The code is easier to refractor and any changes in the code are simpler to implement. This makes reiterative development easier.
- The individual functions can be easily isolated which makes them easier to test out and debug.
However, as with everything, there is also a disadvantage to this approach:
It is new.
What that means is, it is harder to find a Haskell developer than it is to find a C++ and Java developer and it needs to be tested out extensively in real life situations.
The Cardano ICO
The Cardano ICO raised approximately $62 million.
Cardano’s token is named Ada after Ada Lovelace, a 19th century mathematician recognized as the first computer programmer and daughter of the poet Lord Byron.
Cardano’s first major release, named Byron, went live on September 29, 2017, which saw the launch of the Cardano main-net.
Cardano fees
The fees to transfer ADA vary is determined by the following equation:
- transfer fee = a + b * size.
Where:
- a = A constant which currently equals 0.155381 ADA
- b = Another constant that currently equals 0.000043946 ADA/byte
- size = The size of the transaction (in bytes0.
This in effect means that the minimum transaction that you will be paying is 0.155381 ADA and it will increase by 0.000043946 ADA for each byte increase of your transaction size.
In each epoch, the transaction fees are collected in a pool and given to the appropriate slot leaders.
Roadmap of Cardano
According to the roadmap, Cardano will be released in 5 stages:
- Byron: Enables users to trade and transfer Ada. The Cardano mainnet was also launched.
- Shelley: Ensures that the tech is in place for it to become a fully decentralized and autonomous system
- Goguen: Will see the integration of smart contracts.
- Basho: Centered around performance improvements.
- Voltaire: IOHK will add a treasury system and governance.
Cardano’s Trajectory: Current Forecasts and Future Potential
Rising Popularity and Adoption
Cardano, a blockchain platform powered by its native cryptocurrency ADA, has been steadily gaining popularity in the crypto space. With its unique approach to scalability, security, and sustainability, Cardano has garnered attention from both investors and developers alike. Its innovative technology and commitment to peer-reviewed research have positioned it as a promising contender in the blockchain industry.
Growing Ecosystem
One of the key factors contributing to Cardano’s trajectory is its growing ecosystem. The platform boasts a vibrant community of developers who are actively building decentralized applications (dApps) on top of the Cardano blockchain. This expanding ecosystem not only enhances the utility of ADA but also attracts more users and investors to the platform.
The development team behind Cardano is continuously working on improving the infrastructure and adding new features to meet the evolving needs of its users. This commitment to innovation ensures that Cardano remains competitive in an ever-changing market.
Strategic Partnerships
Cardano has also forged strategic partnerships with various organizations across different industries. These partnerships aim to leverage Cardano’s blockchain technology for real-world use cases such as supply chain management, healthcare data management, and identity verification systems. By collaborating with established companies and institutions, Cardano is positioning itself as a viable solution for enterprise-level adoption.
Collaborations with academic institutions allow Cardano to benefit from cutting-edge research in cryptography and distributed systems. This academic approach sets it apart from many other blockchain projects in terms of rigorous scientific foundations.
Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance is another area where Cardano stands out. Unlike some cryptocurrencies that face uncertainty due to regulatory concerns, Cardano has taken a proactive approach by prioritizing compliance with existing regulations. By adhering to legal frameworks, it aims to build trust among regulators and foster mainstream adoption.
Future Potential
Looking ahead, there are several factors that contribute to Cardano’s future potential. The ongoing development of the Goguen era, which will introduce smart contract functionality to the platform, is expected to unlock a multitude of possibilities for developers and users alike. This upgrade has the potential to attract even more projects and investors to the Cardano ecosystem.
Furthermore, Cardano’s commitment to sustainability through its proof-of-stake consensus mechanism sets it apart from energy-intensive alternatives like Bitcoin. As environmental concerns continue to grow, Cardano’s eco-friendly approach may position it as a more attractive option for those seeking sustainable blockchain solutions.
Participating in the Cardano Community
Cardano, a blockchain platform powered by ADA cryptocurrency, offers an opportunity for enthusiasts to become active members of its vibrant community. Engaging with the Cardano community not only allows you to stay updated on the latest developments but also provides avenues for collaboration and learning. Here are some ways you can participate in the Cardano community:
Join Online Forums and Social Media Groups
By joining online forums and social media groups dedicated to Cardano, you can connect with like-minded individuals who share your interest in this innovative technology. Platforms such as Reddit, Telegram, and Discord host active communities where you can engage in discussions, ask questions, and share your insights.
Attend Meetups and Conferences
Attending meetups and conferences related to Cardano is an excellent way to expand your knowledge while networking with industry professionals. These events often feature presentations from experts in the field who provide valuable insights into various aspects of Cardano’s ecosystem. They offer opportunities to meet fellow enthusiasts face-to-face and build connections within the community.
Contribute to Open-Source Development
If you have coding skills or a passion for software development, contributing to open-source projects within the Cardano ecosystem can be immensely rewarding. The project’s GitHub repository is an excellent place to explore existing projects and find areas where you can contribute your expertise. By actively participating in open-source development, you not only enhance your own skills but also contribute towards the growth of the entire community.
Support Stake Pool Operators
Cardano utilizes a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism that relies on stake pool operators (SPOs) to validate transactions on the network. Supporting SPOs by delegating your ADA holdings to their pools helps maintain decentralization and security within the Cardano ecosystem. By doing so, you actively participate in securing the network while earning rewards based on your delegated stake.
Educate Others About Cardano
One of the most significant contributions you can make to the Cardano community is by educating others about its features and potential. Whether it’s through writing blog posts, creating educational videos, or hosting workshops, sharing your knowledge and insights helps raise awareness and fosters a deeper understanding of Cardano among newcomers.
Provide Feedback and Ideas
As a member of the Cardano community, your feedback and ideas are valuable in shaping the future direction of the platform. Participate in discussions on forums, social media groups, and official channels to share your thoughts on improvements, new features, or potential use cases for Cardano. Your input may contribute to the development roadmap or inspire others within the community.
Conclusion
So, there you have it! We’ve journeyed through the world of Cardano, exploring its genesis, unique features, and potential for the future. Cardano stands out as a blockchain platform that combines cutting-edge technology with a thoughtful approach to sustainability, security, and scalability. With its proof-of-stake consensus algorithm, Ouroboros protocol, and emphasis on academic rigor, Cardano has positioned itself as a formidable competitor in the cryptocurrency space.
As you consider your next steps, why not dive deeper into the Cardano community? Join forums, engage with fellow enthusiasts, and stay up to date with the latest developments. Whether you’re an investor looking to stake ADA or a developer interested in creating smart contracts on the platform, Cardano offers a wealth of opportunities. Embrace this evolving ecosystem and become part of the movement shaping the future of finance.
FAQs
Is Cardano a cryptocurrency?
Yes, Cardano is a cryptocurrency. It is a decentralized digital currency that operates on its own blockchain platform called Cardano.
How does Cardano differ from other cryptocurrencies?
Cardano differentiates itself by utilizing a unique proof-of-stake consensus algorithm called Ouroboros. This algorithm ensures security and scalability while minimizing energy consumption.
What is the purpose of the Cardano blockchain?
The primary purpose of the Cardano blockchain is to provide a secure and scalable platform for the development of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts.
Can I stake my Cardano tokens?
Yes, you can stake your Cardano tokens to participate in the network’s consensus mechanism and earn rewards. By staking, you contribute to the security and decentralization of the network.
How can I buy Cardano cryptocurrency?
You can buy Cardano cryptocurrency from various cryptocurrency exchanges. Simply create an account on a reputable exchange, deposit funds, and then trade for ADA, which is the native token of Cardano.








![What is Cardano Blockchain? [The Most Comprehensive Step-by-Step Guide]](https://blockgeeks.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/Sidechains-on-Top-of-Bitcoins-Network_-RSK-Liquid.png)
